Avalanche photodiodes are commercially available that span the wavelength range from 300 to 1700 nm. The rise time tr has a relation with the cut.

A Current Voltage Characteristics B Responsivity And

High Speed Single Photon Detection With Avalanche

Ecstuff4u For Electronics Engineer Avalanche Photo Diode
The corresponding gain value is 65 and the electrical bandwidth is 13ghz at an optical input power of 30dbm.
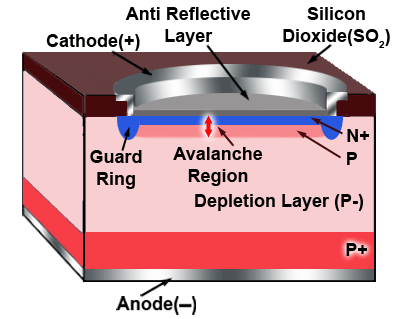
Avalanche photodiode frequency. It is defined as the frequency at which the photodiode output decreases by 3 db from the output at 100 khz. High speed type c5658 can be used over a wide frequency range up to 1 ghz principle of avalanche multiplication the photocurrent generation mechanism of the apd is the same as that of a normal photodiode. The light source used is a laser diode 830 nm and the load resistance is 50 w.
Avalanche photodiodes are used in high bandwidth receiver modules for fiberoptic communication systems to provide greater sn compared to a pin receiver. Rise fall time and frequency response tr tf f3db the rise time and fall time of a photodiode is defined as the time for the signal to rise or fall from 10 to 90 or 90 to 10 of the final value respectively. When light enters a photodiode.
This parameter can be also expressed as frequency response which is the frequency at which the photodiode output. Speed apd avalanche photodiodes and pin photodiodes to a sinewave modulated light input. Avalanche photodiode if a small load resistance r l is used to increase the frequency bandwidth of a pin photo diode the signal voltage may be quite small requiring amplification.
The shortcircuit photocurrent from an avalanche photodiode is calculated using an exact solution of the differential transport equations for the multiplication region. In this work we report a separate absorption charge multiplication gesi avalanche photodiode with an enhanced gain bandwidth product of 845ghz at a wavelength of 1310nm. Silicon apds can be used between 300 to 1100 nm germanium between 800 and 1600 nm and ingaas from 900 to 1700 nm.
Typical fiberoptic systems transmit 1310 or 1550 nm light pulses at 622 mbits or 2488 mbits over single mode fiber and use ingaas detector based receivers. Avalanche photodiode receiver performance metrics introduction the following note overviews the calculations used to assess the noise equivalent power nep noise equivalent input nei and signal to noise ratio stn performance of avalanche photodiodes apds and apd photoreceivers. The dc electric field and the hole and electron velocities are assumed constant in the avalanche region into which photoelectrons are injected.
This can be accomplished with electronic amplifiers but these introduce their own sources of noise and it is sometimes desirable to increase the signal generated by the detector before amplification.
4h Sic Sacm Avalanche Photodiode With Low Breakdown Voltage

Monolithic Germanium Silicon Avalanche Photodiodes With 340
High Gain Bandwidth Product Ge Si Tunneling Avalanche

Working With Avalanche Photo Diode Beginner Problems Q A

Silicon Avalanche Photodiodes From Marktech Optoelectronics

Multiple Quantum Barrier Nano Avalanche Photodiodes Part I

Photodiodes See The Light
Physical Modelling And Experimental Characterisation Of
Physical Modelling And Experimental Characterisation Of

Avalanche Photodiode Polytechnic Hub

Photodiodes

Detectors Guideposts On The Road To Selection Sensors
Comments
Post a Comment